lv overload | dangers of left ventricular hypertrophy lv overload Left ventricle (LV) pressure overload lesions, such as aortic stenosis (valvular, sub-valvular, and supravalvular), coarctation of the aorta (also discussed below), and other conditions associated with systemic hypertension.
Air Malta business class - YouTube. Tony Culshaw. 2.05K subscribers. 61. 6.8K views 1 year ago. Taking off from Luqa in Malta, flying to Zurich, Switzerland on Air Malta in their business.
0 · why is cardiac hypertrophy bad
1 · mild concentric lvh is dangerous
2 · lv overload or aspecific change
3 · lv overload on ekg
4 · life expectancy with lvh
5 · is lvh life threatening
6 · is hyperdynamic left ventricle dangerous
7 · dangers of left ventricular hypertrophy
Product Overview. Round off your grooming routine with the sophisticated scent of Aventus. Presented in a take-anywhere tube bearing Creed's royal three-plume crest this scent opens with tantalising top notes of blackcurrant and Italian bergamot, blended with Calville Blanc apples and sparkling pineapple.
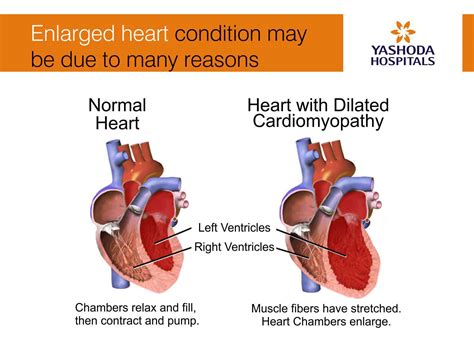
LV hypertrophy is a normal physiologic response to pressure and volume overload. Like any muscle, the heart grows bigger when it is forced to . LVH is a condition where the left ventricle of the heart becomes thick and stiff due to pressure overload. It can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain and heart failure. Learn about the causes, diagnosis and . Uncontrolled high blood pressure is the most common cause of left ventricular hypertrophy. Complications include irregular heart rhythms, called arrhythmias, and heart failure. Treatment of left ventricular hypertrophy depends on the cause. Treatment may include medications or surgery. LV hypertrophy is a normal physiologic response to pressure and volume overload. Like any muscle, the heart grows bigger when it is forced to pump harder. In LV hypertrophy, the muscle fibers in the heart’s main pumping chamber enlarge and, over time, thicken.
why is cardiac hypertrophy bad
mild concentric lvh is dangerous
Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork the heart muscle.Left ventricle (LV) pressure overload lesions, such as aortic stenosis (valvular, sub-valvular, and supravalvular), coarctation of the aorta (also discussed below), and other conditions associated with systemic hypertension.
The left ventricle hypertrophies in response to pressure overload secondary to conditions such as aortic stenosis and hypertension. This results in increased R wave amplitude in the left-sided ECG leads (I, aVL and V4-6) and increased S .
To diagnose left ventricular hypertrophy, a healthcare professional does a physical exam and asks questions about your symptoms and family's health history. The care professional checks your blood pressure and listens to your heart with a device called a stethoscope.
Concentric left ventricular hypertrophy is an abnormal increase in left ventricular myocardial mass caused by chronically increased workload on the heart, most commonly resulting from pressure overload-induced by arteriolar vasoconstriction as occurs in, chronic hypertension or aortic stenosis. Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork the heart muscle. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) refers to an increase in the size of myocardial fibers in the main cardiac pumping chamber. Such hypertrophy is usually the response to a chronic pressure or volume load. The two most common pressure overload states are systemic hypertension and aortic stenosis.
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) makes it harder for the heart to pump blood efficiently. It can result in a lack of oxygen to the heart muscle. It can also cause changes to the heart’s conduction system that make it beat irregularly (arrhythmia).
Uncontrolled high blood pressure is the most common cause of left ventricular hypertrophy. Complications include irregular heart rhythms, called arrhythmias, and heart failure. Treatment of left ventricular hypertrophy depends on the cause. Treatment may include medications or surgery. LV hypertrophy is a normal physiologic response to pressure and volume overload. Like any muscle, the heart grows bigger when it is forced to pump harder. In LV hypertrophy, the muscle fibers in the heart’s main pumping chamber enlarge and, over time, thicken. Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork the heart muscle.Left ventricle (LV) pressure overload lesions, such as aortic stenosis (valvular, sub-valvular, and supravalvular), coarctation of the aorta (also discussed below), and other conditions associated with systemic hypertension.
The left ventricle hypertrophies in response to pressure overload secondary to conditions such as aortic stenosis and hypertension. This results in increased R wave amplitude in the left-sided ECG leads (I, aVL and V4-6) and increased S . To diagnose left ventricular hypertrophy, a healthcare professional does a physical exam and asks questions about your symptoms and family's health history. The care professional checks your blood pressure and listens to your heart with a device called a stethoscope. Concentric left ventricular hypertrophy is an abnormal increase in left ventricular myocardial mass caused by chronically increased workload on the heart, most commonly resulting from pressure overload-induced by arteriolar vasoconstriction as occurs in, chronic hypertension or aortic stenosis.
lv overload or aspecific change
Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork the heart muscle.
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) refers to an increase in the size of myocardial fibers in the main cardiac pumping chamber. Such hypertrophy is usually the response to a chronic pressure or volume load. The two most common pressure overload states are systemic hypertension and aortic stenosis.
Kedvezmények - Agria Park - ahol találkozunk.
lv overload|dangers of left ventricular hypertrophy